Using Quantum Mechanics Describe a Particle in a Box Model
Note that the different allowed energies are labeled by the quantum number n which can only take on integer values. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.

Physics Ch 66 Ch 4 Quantum Mechanics Schrodinger Eqn 19 Of 92 Particle In 1 D Box Example 1 2 Youtube
If the probability of finding a quantum particle at the midpoint is zero the particle is never at this point right.

. Using the particle in a box model to describe why. And it hasnt completely lost the ability to provide new insights. The logic of the resolution can seem disconcerting at first sight.
And thats why length of the boxes correlated this way with the energy in a quantum box. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. Inside the semiconductor used in microelectronics there are small particles of.
Okay so when we have a greater a large box the energy is much more smaller. The quantum particle in a box model has practical applications in a relatively newly emerged field of optoelectronics which deals with devices that convert electrical signals into optical signals. The box is completed by applying a similar repulsive force at so that the probability of finding the particle at locations is also extremely small.
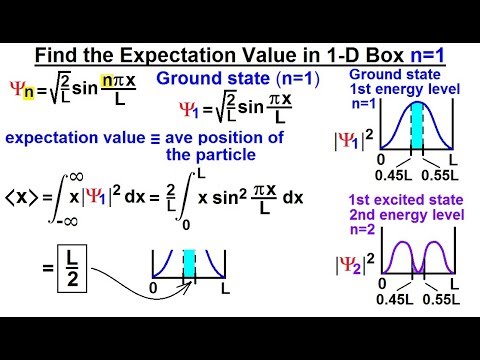
A 00251 a2 b a24. In classical systems for example a particle trapped inside a large box can move at any speed within the box and it is no. BFind the expectation value x of the particles position.
The potential energy is zero inside the box but rises abruptly to infinity at the walls. The first problem often treated in class is that of a quantum particle in a one dimensional unescapable box. So to change the mode of vibration we need much more energy.
The boundaries at these locations are infinetly high trapping the electron within these boundaries at x0 and xL. This wave is related to the probability of finding. Because those are very simple to find.
We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts. For this model the particle an electron is confined within a length x which ranges from 0 to L. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook.
Textbook solution for University Physics Volume 3 17th Edition William Moebs Chapter 7 Problem 14CQ. This model can be used to determine the wavelength of maximum absorption max in conjugated molecules. Is easier to describe the modes of vibration inside.
This model also deals with nanoscale physical phenomena such as a nanoparticle trapped in a low electric potential bounded by high-potential barriers. Using the quantum particle in a box model describe how the possible energies of the particle are related to the size of the box. Thats why the equation is this one.
These energies can be qualitatively understood by considering the wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics wherein objects we normally think of as particles in some ways behave as waves and vice-versa. One looks at so-called stationary quantum wave states and depending on the state determine for instance the energy of the particle and its probability to be a certain point in space the. The 15th video in this introductory course in quantum mechanics looking at the position and momentum probabilities for a particle confined to a one dimensio.
The Particle in a Box model of quantum mechanics addresses and isolates translational motion. Quantum Dots as a Particle in a Box The problem of quantum mechanics which corresponds to the Particle in a Box is a rather difficult thing to display. The particle in a two-dimensional box extends the particle in a box concept to two dimensions.
How does it come then. This is because until now there was not a real good example of such a system. This is most commonly modeled as an electron moving along a conjugated chain.
Particle-in-a-box is useful because it is one of the easiest problems to solve in quantum mechanics and because you can see many of the routine features of QM like orthogonal basis states wave functions with nodes etc clearly and easily. Solutions for Chapter 7 Problem 14CQ. In quantum mechanics the particle in a box model describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers.
For example it is easy to show that the kinetic energy of a wave. Quantum Mechanics of Particle-in-a-Box Models We are about to show you how to solve the Schrodinger equation for a simple but important model for which we can carry out every step of the complete solution using only simple mathematics. Solving the Schrödinger equation for this simple one-dimensional particle-in-a-box system yields the following allowed energies.
Quantum Mechanics Lecture-8 Concept of Modern Physics by A. This model also deals with nanoscale physical phenomena such as a nanoparticle trapped in a low electric potential bounded by high-potential barriers. Beiser Page 1 Exercise.
Unsurprisingly they find stationary states and have no time dependence. Where h is Plancks constant m is the particle mass and L is the one-dimensional length. We will convert the equations into graphical form and use the graphs to provide physical interpretations of the solutions.
The quantum particle in a box model has practical applications in a relatively newly emerged field of optoelectronics which deals with devices that convert electrical signals into optical signals. Thats not really a feature of Quantum Mechanics just of the simple illustrative example. This means that an electron in a box must be described as a wave in quantum mechanics with wavelength λhp.
In quantum mechanics a particle in a box model describes a particle of mass m confined between two walls at x0 and x-L. Kuhn in 1949 first proposed to use this. A Particle limited to the x-axis has the wave function ax between x0 and x1.
11 It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry quantum field theory quantum technology and quantum information science. If the energy of a particle-in-a-box is. With Quantum Dots the situation has changed.
For a quantum particle in a box the first excited state Ψ 2 Ψ 2 has zero value at the midpoint position in the box so that the probability density of finding a particle at this point is exactly zero. It uses quantum numbers n and k for the levels along the x-axis and y-axis respectively some authors use nx and ny for these numbers. The ubiquitous particle in an infinite square well examples are using the time-independent Schroedinger equation to look for stationary states.
Explain what is wrong with the following reasoning. It still contains a single particle. Using the particle in a box model to describe why things have color - GitHub - milton900807quantum-mechanics.
AFind the probability that the particle can be found x045 and x055. However this particle lies on a plane surrounded by walls of infinite potential. In general in quantum mechanics we cannot make these probabilities go exactly to zero but we can consider the idealization that the forces are sufficiently strong to make the probabilities as close to zero as we like.
Physics Ch 66 Ch 4 Quantum Mechanics Schrodinger Eqn 27 Of 92 Expectation Value 1 D Box N 1 Youtube

Introductory Quantum Chemistry The Course Will Introduce Quantum Mechanics As Applied To Chemist Introduction To Quantum Mechanics Quantum Mechanics Chemistry

No comments for "Using Quantum Mechanics Describe a Particle in a Box Model"
Post a Comment